Upgraded Environmental Regulations: How to Comply with Processing Wastewater Disposal
Upgraded Environmental Regulations: How to Comply with Processing Wastewater Disposal
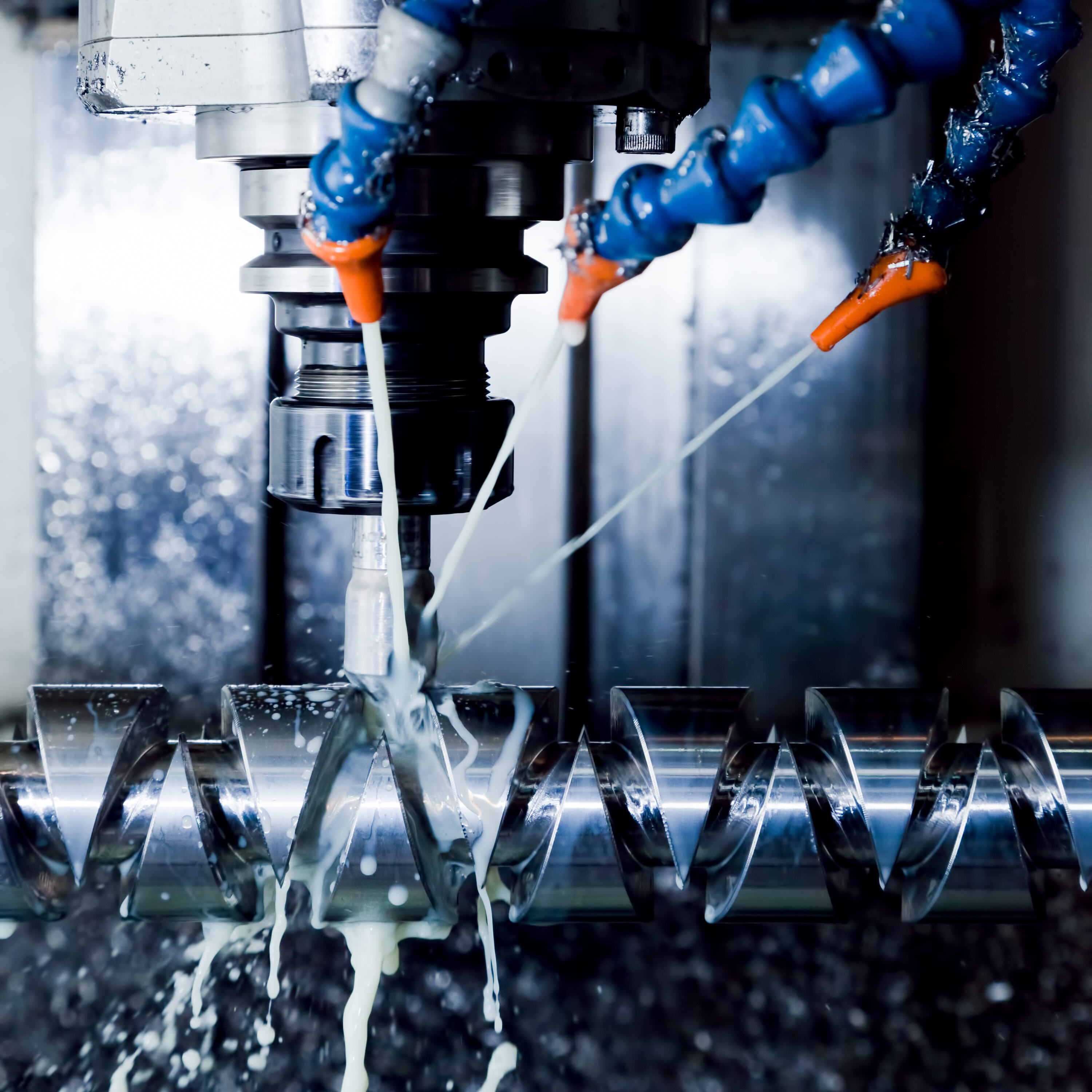
When the new environmental inspector walked into our machining workshop last quarter, the air instantly grew tense. We had just completed a large batch of aluminum parts, and the wastewater tank was full. With stricter local and international environmental regulations now in force, we knew that even a small oversight in wastewater treatment could result in heavy fines—or worse, production suspension.
For many factories, wastewater disposal is no longer a “backstage” task handled by a few technicians. It’s a compliance issue that directly affects production continuity, certification status, and business reputation. Here’s how we (and you) can stay compliant under the latest upgraded environmental standards.
1. Understand What Changed in Environmental Regulations
The latest updates to industrial wastewater regulations—especially after 2024—tighten the limits for chemical oxygen demand (COD), suspended solids (SS), and heavy metal content.
If your plant processes aluminum, stainless steel, or titanium, the following thresholds are now common benchmarks:
| Parameter | Previous Limit | New Limit (2025) | Common Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| COD | ≤ 120 mg/L | ≤ 80 mg/L | Coolant & cutting oil residues |
| SS | ≤ 80 mg/L | ≤ 50 mg/L | Metal fines from machining |
| pH | 6–9 | 6.5–8.5 | Chemical degreasing fluids |
| Cu / Ni | ≤ 1.0 mg/L | ≤ 0.5 mg/L | Electroplating, stainless machining |
Pro Tip: Keep these limits visible on your wastewater treatment control board. Many audit failures happen simply because the operator isn’t aware of updated standards.
2. Step-by-Step: How to Comply with Wastewater Disposal Regulations
Complying isn’t just about installing a treatment system—it’s about managing every stage efficiently.
Step 1. Identify Wastewater Sources
Start with an internal audit. In CNC machining, major sources include:
-
Coolant and cutting oil waste from lathes or milling machines
-
Rinse water from anodizing or plating lines
-
Equipment cleaning liquids containing surfactants
Use flow meters or daily volume logs to quantify each source.
Step 2. Pre-Treatment Separation
Before the main treatment, use oil–water separators or magnetic filtration systems to remove large contaminants.
We recently replaced our traditional skimmer with a coalescing oil separator—resulting in a 38% drop in COD before the secondary treatment stage.
Step 3. Chemical Treatment and Neutralization
Use pH adjustment tanks and flocculants (e.g., PAC or PAM) to bind suspended particles.
Run a jar test weekly to adjust chemical dosage based on pH and conductivity readings.
Step 4. Sludge Dewatering & Disposal
After precipitation, sludge moisture should be reduced below 80% using a filter press.
Partner with certified waste disposal agencies and keep digital records—environmental audits now often require QR-coded disposal certificates.
Step 5. Continuous Monitoring
Install online COD/pH sensors connected to a SCADA or cloud dashboard. This not only simplifies reporting but also helps prevent violations in real time.
3. Technology Solutions to Simplify Compliance
With the rise of smart manufacturing, wastewater treatment is also becoming more automated.
We implemented a small IoT-based wastewater control system that:
-
Automatically doses neutralizing chemicals when pH drifts.
-
Sends real-time data to our compliance officer’s phone.
-
Generates monthly wastewater reports automatically.
As a result, our compliance report preparation time dropped from 2 days to under 4 hours.
If your factory hasn’t yet integrated monitoring systems, start small: add flow sensors, automatic data loggers, and pH alarms to your existing tanks.
4. Cost and Efficiency Balance: What to Consider Before Upgrading
Many procurement teams worry about high costs when upgrading wastewater systems. Here’s how to optimize ROI:
| Upgrade Item | Approx. Cost (USD) | Expected ROI | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smart pH Controller | $800–1,200 | 1.5 years | Prevents overuse of neutralizers |
| Oil–Water Separator | $1,000–1,500 | 2 years | Reduces COD & fines |
| Filter Press | $3,000–5,000 | 3 years | Cuts sludge volume by 40% |
| IoT Monitoring Unit | $1,500 | 1 year | Simplifies reporting & audits |
Tip for buyers: Choose suppliers who can provide both equipment and on-site installation training. In our experience, untrained staff cause 60% of post-installation issues.
5. Final Checklist for Wastewater Compliance (2025 Edition)
Before your next inspection, make sure you have:
-
✅ Monthly COD, SS, and pH test records
-
✅ Certified disposal partner contracts
-
✅ Emergency spill prevention plan
-
✅ Updated training logs for operators
-
✅ Backup wastewater flow data (digital or printed)
Staying compliant isn’t just about avoiding penalties—it’s about building a sustainable, trustworthy brand. As global customers increasingly evaluate supplier ESG performance, wastewater management has become a clear sign of manufacturing credibility.
Compliance as a Competitive Advantage
When we first upgraded our wastewater system, we saw it only as a regulatory requirement. But within months, it became part of our customer value proposition. Several overseas clients, including those in Germany and Japan, specifically chose us because we could demonstrate traceable, compliant wastewater handling.
In today’s manufacturing world, compliance is no longer optional—it’s a marketing advantage.
So, if you’re preparing for the next round of environmental audits, start with your wastewater system. A clean discharge isn’t just good for the planet—it’s good for business.
PFT Precision,Your Trusted Partner in Custom CNC Machining
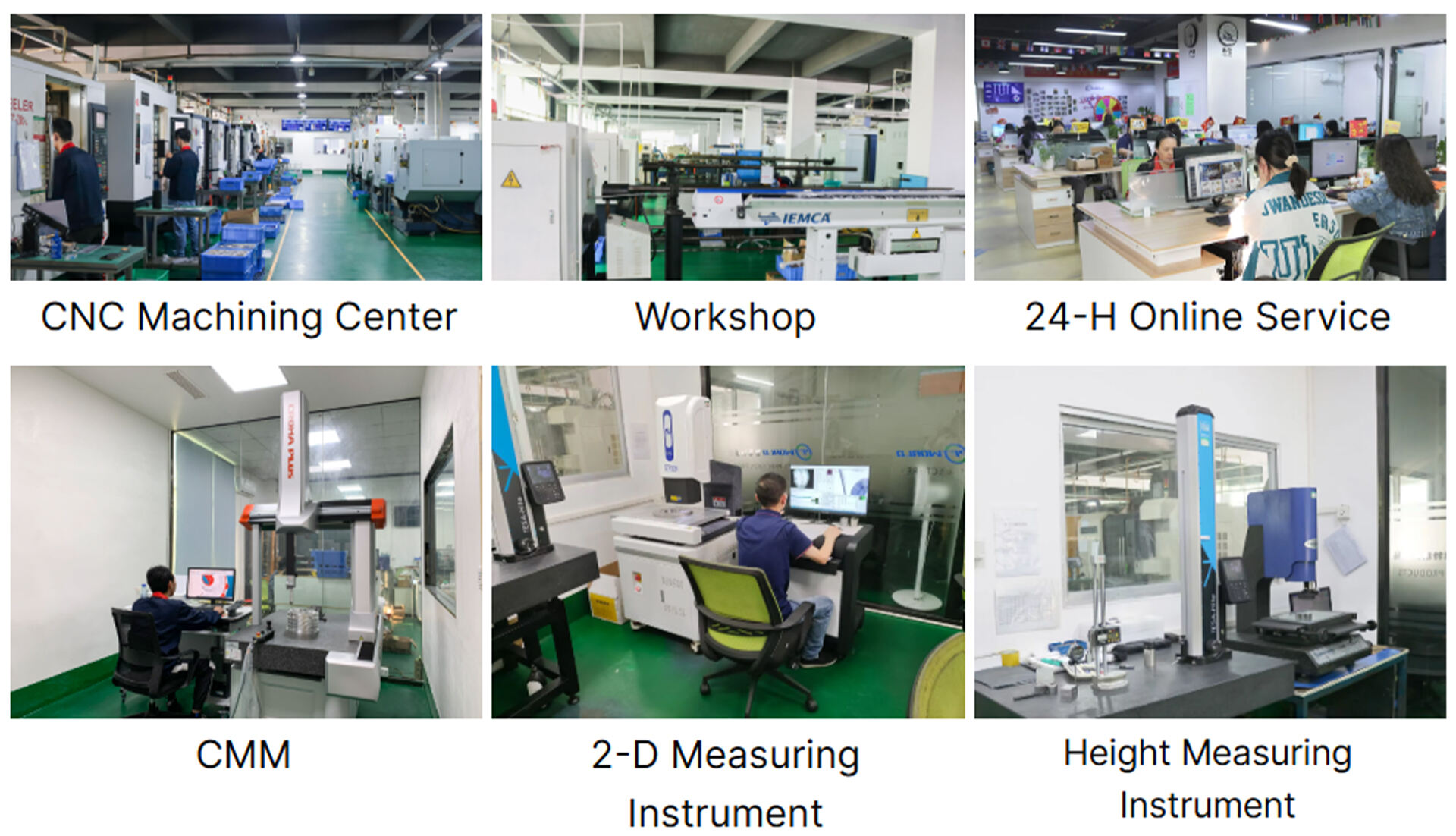
As a leading provider of custom CNC machining parts and components, PFT Precision specializes in prototype turning and milling using high-quality metal materials. We deliver precision-engineered products tailored to the unique requirements of various industries. Our commitment to excellence has established us as one of the top CNC manufacturing suppliers in the market.
We are proud to hold several production certificates for our CNC machining services, which demonstrates our commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. Our team follows strict quality control procedures to ensure that every part we produce meets the highest standards of quality and accuracy
|
Processing
|
CNC Turning, CNC Milling, Laser Cutting, Bending, Spining, Wire Cutting, Stamping, Electric Discharge Machining (EDM), Injection Molding
|
|||||||
|
Materials
|
Aluminum: 2000 series, 6000 series, 7075, 5052, etc
|
|||||||
|
Stainlesss steel: SUS303, SUS304, SS316, SS316L, 17-4PH, etc
|
||||||||
|
Steel: 1214L/1215/1045/4140/SCM440/40CrMo, etc
|
||||||||
|
Brass: 260, C360, H59, H60, H62, H63, H65, H68, H70, Bronze, Copper
|
||||||||
|
Titanium: Grade F1-F5
|
||||||||
|
Plastic: Acetal/POM/PA/Nylon/PC/PMMA/PVC/PU/Acrylic/ABS/PTFE/PEEK etc
|
||||||||
|
Surface Treatment
|
Anodized, Bead Blasted, Silk Screen, PVD Plating, Zinc/Nickl/Chrome/Titanium Plating, Brushing, Painting, Powder Coated, Passivation, Electrophoresis, Electro Polishing, Knurl, Laser/Etch/Engrave etc
|
|||||||
|
Tolerance
|
±0.002 ~ ±0.005mm
|
|||||||
|
Surface Roughness
|
Min Ra 0.1~3.2
|
|||||||
Trust the Experts in CNC Machining
Aluminum
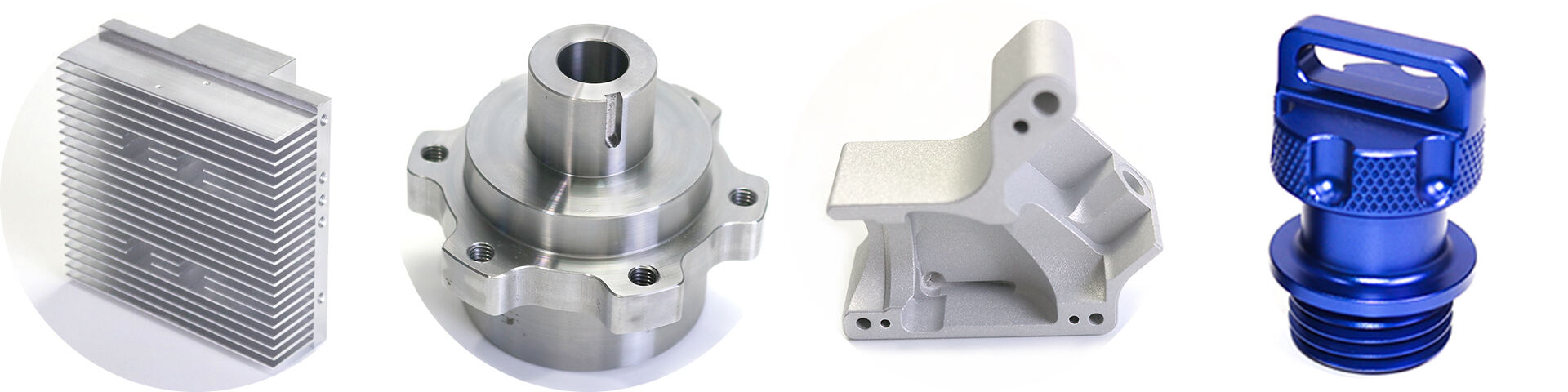

Stainless Steel/Steel/Titanium Alloy
1214L/1215/1045/4140/SCM440/40CrMo, etc
TA1, TA2/GR2, TA4/GR5, TC4, TC16, TC18, TC21, TC22, TC26, TC118B etc

Brass/Copper

Plastic

CNC Machined Parts Surface Treatment.
Detailed drawings (PDF/STEP/IGS/DWG...), including quality, delivery date, materials, quality, quantity, surface treatment and other information