Building 49, Fumin Industrial Park, Pinghu Village, Longgang District
Sunday Closed
Type:Broaching, DRILLING, Etching / Chemical Machining, Laser Machining, Milling, Other Machining Services, Turning, Wire EDM, Rapid Prototyping
Model Number:OEM
Keyword:CNC Machining Services
Material:stainless steel aluminum alloy brass metal plastic
Processing method :CNC milling
Delivery time:7-15 days
Quality:High End Quality
Certification:ISO9001:2015/ISO13485:2016
MOQ:1Pieces
In today’s manufacturing landscape, CNC precision parts play a foundational role in delivering high-quality, efficient, and repeatable machining results. As industries push the boundaries of design complexity and performance expectations, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining has emerged as the standard for producing intricate parts with micron-level accuracy.
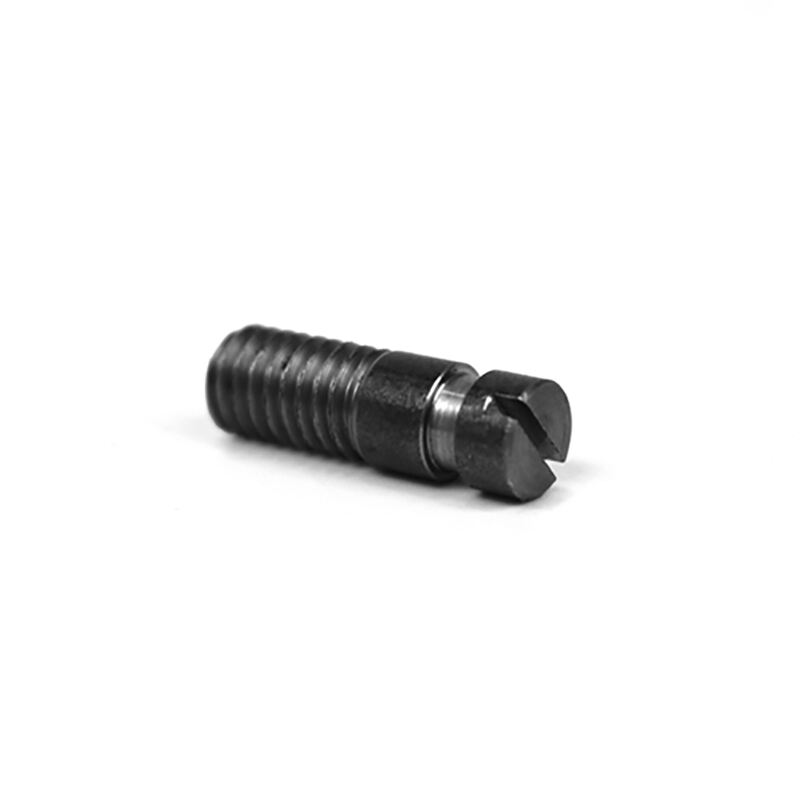

CNC precision parts refer to components manufactured using CNC machining processes where computer-aided tools control lathes, mills, grinders, and other cutting machinery to achieve exact specifications. These parts are designed with tight tolerances—often within a few microns—and are integral to industries where precision and durability are non-negotiable, such as aerospace, medical, automotive, and electronics.
CNC machining starts with a digital CAD (Computer-Aided Design) model, which is converted into a CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) file. This file directs the machine’s movements in terms of speed, direction, depth, and tool paths. With multi-axis capabilities (such as 3-, 4-, and 5-axis machines), CNC machining can produce highly complex shapes that are difficult or impossible to achieve through manual methods.
1. High Accuracy and Consistency
One of the most prominent benefits is the repeatability of CNC-machined parts. Once a program is created and validated, it can produce thousands of identical components with minimal variation.
2. Complex Geometry
CNC machines can produce parts with intricate geometries, deep cavities, tight radii, and complex surface contours that traditional machining cannot match.
3. Material Versatility
CNC machining supports a broad range of materials including metals (aluminum, titanium, stainless steel), plastics (POM, ABS, PTFE), and even composites. This flexibility makes CNC precision parts suitable for various functional and aesthetic applications.
4. Efficiency and Speed
Modern CNC systems can operate 24/7 with minimal supervision. This not only improves production speed but also reduces labor costs and downtime.
5. Reduced Waste
Precision machining ensures optimal use of raw materials, reducing scrap rates and increasing sustainability in the manufacturing process.
Aerospace: Components like turbine blades, engine mounts, and landing gear parts require tight tolerances and exceptional reliability.
Medical: Surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and diagnostic device components must be flawless and biocompatible.
Automotive: Engine parts, transmission housings, and custom performance components benefit from CNC precision for improved performance and safety.
Electronics: CNC machining produces housings and connectors for smartphones, computers, and IoT devices where precision ensures functionality and durability.
As Industry 4.0 reshapes manufacturing, CNC precision machining is evolving with innovations like real-time monitoring, AI-driven predictive maintenance, and integration with 3D printing and additive manufacturing. The demand for miniaturized and lightweight components will further drive the need for ultra-precision machining technologies.


Q:What materials can be used in precision fabrication?
A:A wide variety of materials can be used, including:
· Metals: Aluminum, stainless steel, carbon steel, titanium, brass, copper
· Plastics: ABS, polycarbonate, acrylic, nylon, POM (Delrin)
· Composites: Carbon fiber, fiberglass
Material choice depends on the application’s structural, thermal, or chemical requirements.
Q:What is the typical turnaround time for precision fabrication?
A:Turnaround time varies based on complexity, volume, and material availability. Prototypes may take a few days to a week, while full production runs may range from 2 to 6 weeks. Some providers offer expedited services for urgent projects.
Q:What is the difference between precision fabrication and traditional metal fabrication?
A:Precision fabrication involves tighter tolerances, more advanced equipment (like CNC machines and laser cutters), and stricter quality control than traditional fabrication. It focuses on high-performance applications where even small deviations can cause system failures.
Q:Do you offer custom or one-off fabrication?
A:Yes. Most precision fabrication providers offer custom fabrication for both prototypes and one-off parts. CAD drawings or design files are typically required to begin the process.
Q:Can you handle large-scale production?
A:Absolutely. While many shops specialize in prototypes and small batches, others are equipped for high-volume production with consistent quality through automation, CNC machining, and robotic welding.
Q:What types of finishes can be applied to fabricated parts?
A:Common finishing options include:
· Powder coating
· Anodizing
· Electroplating
· Sandblasting or bead blasting
· Brushing and polishing
· Painting or silk-screening
These finishes improve durability, corrosion resistance, or visual appeal.
Q:What file formats are accepted for fabrication projects?
A:Most providers accept CAD files such as:
· .STEP / .STP
· .IGES / .IGS
· .DXF
· .DWG
· .PDF (for drawings)
It's best to confirm with your fabricator for preferred formats.
Q:How is quality controlled in precision fabrication?
A:Quality control methods include:
· CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) inspections
· Laser scanning
· In-process dimensional checks
· Surface roughness testing
· Visual inspection and functional testing
Certifications such as ISO 9001 or AS9100 often indicate a higher standard of quality assurance.
Copyright © Shenzhen Perfect Precision Products Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved — Privacy Policy — Blog